Dobutamine stress echocardiography
What is an echocardiogram (echo)?
An echocardiogram (also known as an echo) is a test that uses sound waves to build up a moving picture of the heart. It is similar to the ultrasound scan used in pregnancy.
What is a dobutamine (stress) echo?
A dobutamine (stress) echo combines a normal echo with a drug (dobutamine) which has similar effects to exercise on the heart and circulation. It works by increasing the heart rate and the strength of its contractions without the need for exercise.
Performing an echo during exercise can help doctors to find the cause of the symptoms you may experience during physical stress or exercise. It is sometimes difficult to get high-quality pictures of your heart during exercise because of deep breathing and movement. Some patients are also unable to do the exercise (stress) echo due to problems walking on a treadmill so an alternative is to use dobutamine.
How is the test performed?
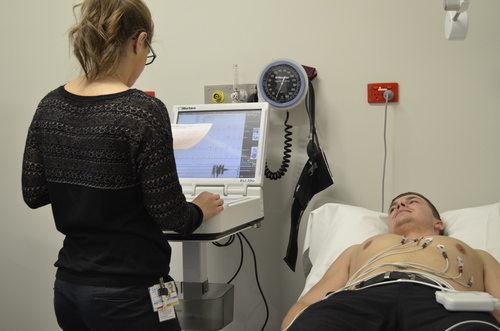
We will ask you to remove your clothes from the waist up and to lie on an echo bed. We will attach 12 small sticky patches, called electrodes, to your chest so we can record your echo and the electrical activity of your heart (electrocardiogram or ECG).
A small plastic tube (cannula) will be inserted into a vein in your arm. We will take the first echo and then inject a very low dose of dobutamine through the cannula in your vein. We will increase the drug in small doses every three minutes. During the test, you will gradually notice your heart beating faster and more strongly as if you were exercising.
Once you have reached your target heart rate (calculated based upon your age), the drug will be stopped. The doctor may also stop the drug early if you develop certain symptoms such as chest discomfort, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness or there are significant changes in your blood pressure or ECG. Ultrasound images will be taken at four stages throughout the testOnce all images are obtained the drug infusion will be ceased and your heart rate will return to normal resting rate. The effects of the drug will wear off in around 5 minutes.
How do I prepare for the test?
You may need to stop specific heart medicines one or two days before the test. We will advise you when you book your appointment. If you are unsure, please ask. We suggest that you do not eat a heavy meal in the two hours before your test.
How long does the test take?
The test can take up to an hour, including preparation and recovery time. Once you feel recovered, you can usually go straight home.
What are the benefits of having the test?
The test helps doctors to find the cause of symptoms from physical stress or exercise in patients who cannot do an exercise test. It produces high-quality images without the interference of deep breathing and muscle tremors from exercise. It is also used to check if certain parts of the heart have been permanently damaged after a heart attack or if some recovery is possible. This information may help in managing your treatment.
What are the risks of having the test?
There are no known serious risks from the clinical use of ultrasound for scanning. The dobutamine (stress) test is very safe and widely used in patients with chest pain or patients with symptoms that limit their ability to exercise.
A small number of patients may experience flushing of the face and / or minor palpitations, both of which go away very quickly once the test is stopped. You may also notice symptoms that you would otherwise have developed during normal exercise, such as chest pain, breathlessness, or dizzy spells, which usually go away once the test is stopped.
Dobutamine (stress) echo is widely used in patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease. There is a very small risk of serious side effects such as heart attack or stroke in these patients and the medication can cause heart rhythm disturbance. Fortunately, serious side effects are very rare.
Please notify the doctor immediately if you are:
- pregnant or think that you may be pregnant (there is a risk of injury to the foetus from dobutamine)
- lactating or breast feeding
- allergic or sensitive to medications or latex.
Is there an alternative test available?
The exercise (stress) echo is an alternative test if you are able to exercise, but it may be more difficult to get high-quality images of the heart after exercise. Your cardiologist has requested this test because he or she believes it will help to diagnose your condition and/or decide on your treatment better than other tests can. Please discuss any concerns you may have about the test with your cardiologist.